By Mike Brown, LendEDU
Special to the Financial Independence Hub
Americans struggling to repay their 2019 taxes in the midst of a recession has been just another issue to deal with during the coronavirus pandemic.
Recognizing this, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) actually extended the filing and payment deadline for 2019 tax obligations from April 15, 2020, to July 15, 2020.
The extension may have temporarily stopped the bleeding, yet there’s a looming tax debt crisis that has the potential to boil over in 2021 when 2020 taxes are due.
That’s because millions of Americans took to relying on unemployment benefits, retirement funds, or stock sales to stay afloat amidst the pandemic recession.
All of those things could lead to a heavier tax obligation in 2021, and with many people still out of work and struggling to get by, the country could be looking at staggering tax debt numbers next year.
The U.S. tax gap (total outstanding tax debt) currently hovers around $400 billion, but that figure could approach crisis levels after next year’s tax season.
To capture the struggles from the 2020 tax season and also the fears regarding the 2021 tax season, LendEDU surveyed 1,000 adult Americans to better understand what the average taxpayer has been dealing with during these unprecedented times.
Observations & Analysis
All data is based on an online survey of 1,000 adult Americans commissioned by LendEDU and conducted by research firm Pollfish. The survey was conducted on December 1, 2020. For some questions, the answer percentages may not add up to 100% exactly due to rounding.
17% of Americans laid off because of Pandemic unable to pay all 2019 Taxes
As mentioned above, the IRS extended the deadline to pay 2019 taxes by three months given the financial hardships experienced by many as a result of the coronavirus pandemic and recession.
However, paying all taxes owed by the July 15th deadline was still impossible for many Americans, especially those who have lost jobs due to the pandemic.
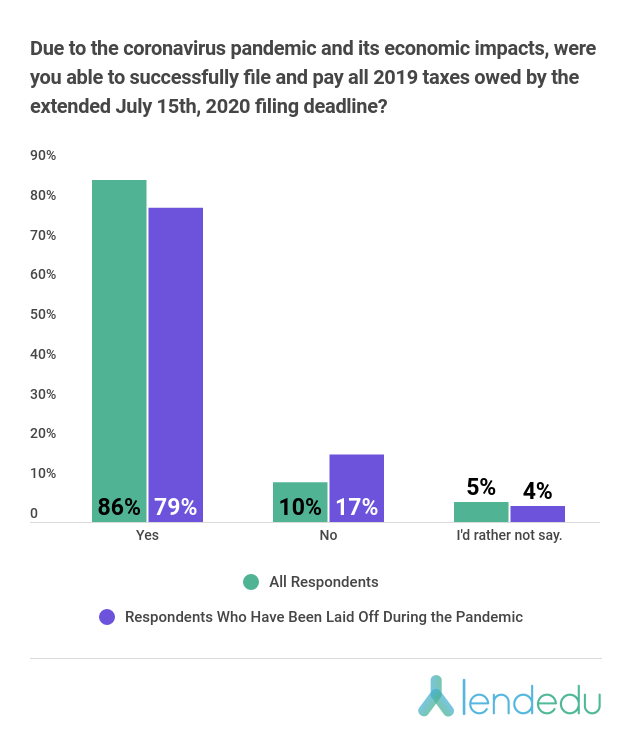 Amongst respondents who have lost their jobs during the coronavirus pandemic, 17% were not able to pay their 2019 taxes on time and in full.
Amongst respondents who have lost their jobs during the coronavirus pandemic, 17% were not able to pay their 2019 taxes on time and in full.
Many still haven’t filed Tax Returns
Even if you are unable to fully pay all tax obligations by the filing deadline during any given year, you should always file your tax returns on time.
When dealing with the IRS, a failure-to-file penalty is much worse (5% of unpaid taxes for each month your tax return is late, up to 25%) then a failure-to-pay penalty (.5% of unpaid taxes for each month you don’t pay, up to 25%).
Yet still, data from our survey found many Americans that couldn’t pay all their taxes on time also didn’t file on time.
32% of taxpayers who couldn’t pay all 2019 taxes on time didn’t file their taxes by July 15th either. Even worse, 72% of these taxpayers who missed the July 15th filing deadline still have yet to file their tax returns for 2019, which could lead to serious financial and legal troubles.
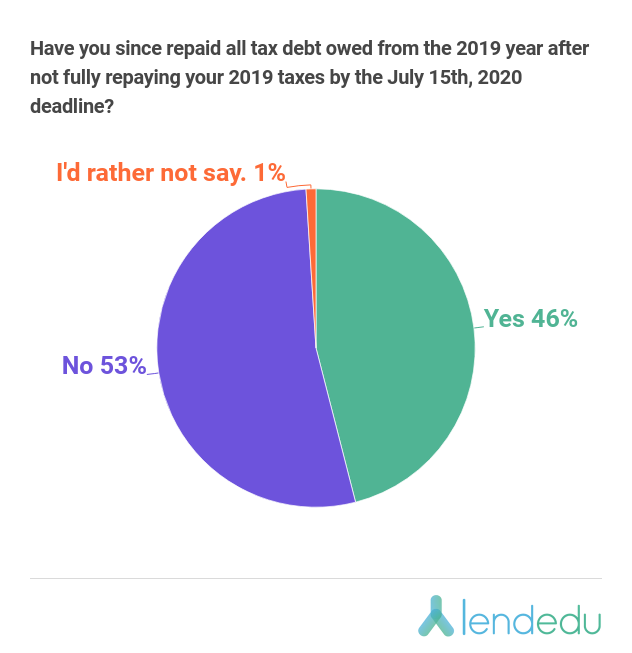
Amongst respondents who at least have filed their 2019 tax returns despite not being able to fully pay all taxes by July 15th, here’s how many have been able to finally repay all 2019 taxes owed…
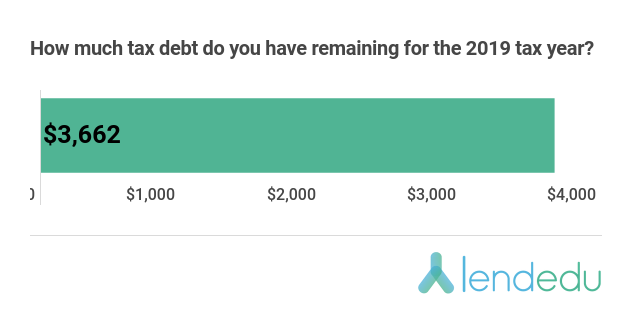
With 53% of applicable taxpayers still having tax debt from 2019, we wanted to see how much they have left…
For American taxpayers that still have some amount of tax debt from the 2019 tax year, the average amount remaining is $3,662.
If you are someone that is currently repaying tax debt, you may want to learn more about tax relief as a possible way to settle or reduce your tax bill.
The data from our survey makes it clear that repaying 2019 taxes has been unusually tough, and mass unemployment brought on by the coronavirus pandemic has been a big reason for the struggles.
But the coronavirus pandemic’s impact on the tax system won’t end in 2020 and likely will be more damaging in 2021 as taxes from this unprecedented year will be owed.
Over half worried about next year’s Tax Debt
The 2021 tax season is shaping up to be a brutal one as the full financial ramifications of the coronavirus pandemic and recession develop. Continue Reading…