As consumers we prefer higher quality things, and with stocks it may be no different. Learn why Quality may be important to investors.

By Erin Allen, Vice President, Direct Distribution, BMO ETFs
(Sponsor Blog)
Quality is a very familiar concept in society. As we know, an item can’t be judged on price alone. If one shirt costs $10, versus another that costs $30, does this mean the cheaper shirt is better based on price alone? Most likely not, as what matters is the quality of the shirts, and how it will perform in the future!
In investing, Quality is no different. It starts with a base assumption that all stocks aren’t created equal, some are going to be higher quality than others, and as a result may enjoy better risk-adjusted returns. As consumers we prefer higher-quality things, and with stocks it is no different. Indeed, higher-quality stocks have historically shown benefits to investors, outperforming over time.[1]
What makes a company a quality company?
There are different approaches to identifying Quality, with associated pros and cons. Warren Buffett prefers to look for companies with “competitive moats” and companies that exhibit earnings power in excess of its peers. If a business model is easily replicated, one would expect copycats to soon enter, and drive down profitability. Companies with competitive moats have advantages that competitors find difficult to touch, and would be considered higher quality. Many fundamental investors have a Quality screen in place and will also often look for high-quality management teams, which are assessed by in-person meetings, and other heuristics.
Quality can also be defined by assessing financial metrics in a consistent and disciplined approach. This is an approach BMO GAM has taken for the ETFs listed below, using the MSCI index which BMO’s Quality ETFs are based. Three metrics are assessed: ROE (Return on Equity), Leverage (Debt to Equity), and Earnings stability (the consistency of earnings through time). Having discipline, and a regular rebalancing schedule to assess and make changes, is of tremendous benefit in investing, to mitigate the role of emotion and behavioural biases, and to ensure the portfolio remains on plan, and true to its intended exposure.
ROE – This is a measure of profitability. Companies with higher profitability are winners in their respective industries. In investing, while things do evolve over time, winners tend to remain winners*1. Higher profitability is a good signal a company has a high-Quality business model.
Low Leverage – High Quality companies tend to be cash rich, from driving solid and consistent business results. Apple is a great example, as it is currently sitting on over US$60 billion of cash and short-term investments2. In short, Quality companies often have less need for debt, so BMO GAM screens for companies with less debt overall.
Earnings Stability – Companies with strong competitive advantages tend to have more consistent earnings streams, as competitors find it difficult to take a “bite out of their lunch.” Quality companies tend to show their merits in earnings consistency through time.
When does Quality tend to perform well, and when may it lag?
Quality companies tend to have a risk level at or slightly below broad markets, and can participate in growth, while maintaining a measure of defensiveness should volatility in markets increase. Investing in higher-profitability stocks tends to give the quality exposure a growth flavour, while in negative equity markets quality stocks will often be preferred due to their strong overall balance sheet strength, with less debt and more consistent earnings. As well, higher interest rate environments tend not to be as much a concern for quality companies, as their debt levels are lower and they are less exposed to higher interest rate impacts.3
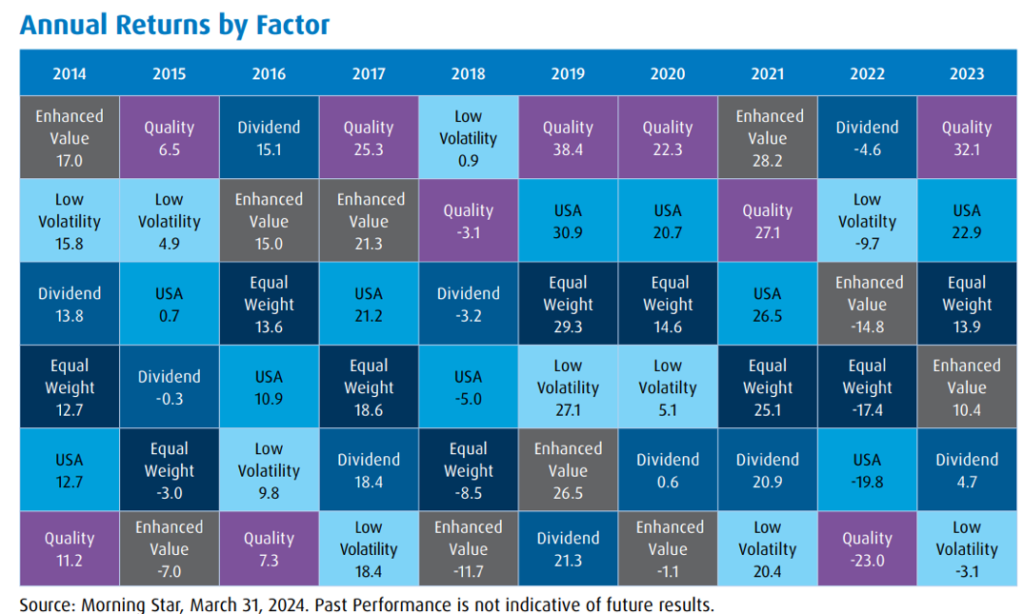
Performance wise, like all factors, Quality is best evaluated versus broad market performance through the entire market cycle, or market cycles. However, as a generalization, Quality stocks tend to do well in growth markets. In very strong bull markets Quality stocks tend to participate well, but higher risk/lower quality stocks may outperform when investors are the most exuberant and take on more risk. In backdrops with higher market volatility, Quality tends to outperform, as company fundamentals and balance sheet strength matter. These are general historical performance trends, and performance in specific market scenarios may vary.
The chart below illustrates factor performance over the past 10 years which shows quality outperforming in many years.
Other considerations
Implementing a quality exposure in your portfolio leads to sector differences and security differences versus the broad index. For example, in the U.S., Quality tends to overweight Technology companies, as many of these companies fit the bill of high profitability/low debt/consistent earnings, and underweight other sectors such as Consumer Discretionary, where the metrics are not as strong. Continue Reading…