Special to the Financial Independence Hub
Stock market volatility can and will happen, which can really spook many investors.
To help with that, should you use an all-weather portfolio for changing market conditions?
Would an all-weather portfolio be best long-term?
How would I build an all-weather portfolio using Canadian ETFs?
Read on and find out our take, including the pros and cons of this all-weather investing approach.
The portfolio is designed for all seasons
If you prefer a more passive approach to investing, building an all-weather portfolio may be right for you. While this portfolio is designed to perform well during all seasons of the market, from an economic boom or bust and the messy stuff in between, we’ll see below that this approach is not without some flaws and drawbacks – just like any investing approach. Further, you could be missing out on some important aspects or assets for investing entirely.
Understanding how an all-weather portfolio works can help you to decide if this path could be right for you, or even if a blended all-weather approach could make much more sense.
What Is an All-Weather Portfolio?
Just as the name sounds, an all-weather portfolio is a portfolio that’s built to do well, regardless of changing market conditions.
This investing approach was popularized by Ray Dalio, a billionaire investor and founder of Bridgewater Associates, the largest hedge fund in the world. At the time of this post, Bridgewater currently manages over $140 billion in assets.
(FYI – this sounds very impressive of course, but we don’t invest in hedge funds and neither should you!)
Dalio’s all-weather philosophy is largely this:
Diversify your investments, hold specific asset classes in certain allocations, such that the portfolio can perform consistently throughout most economic conditions.
This includes periods of increasing volatility, rising inflation, and more. More specifically, this portfolio strategy is designed to help investors ride out four specific types of events:
- Inflationary periods (rising prices)
- Deflationary periods (falling prices)
- Rising markets (bull/booming markets)
- Falling markets (bear/busting markets)
How an All-Weather Portfolio Works
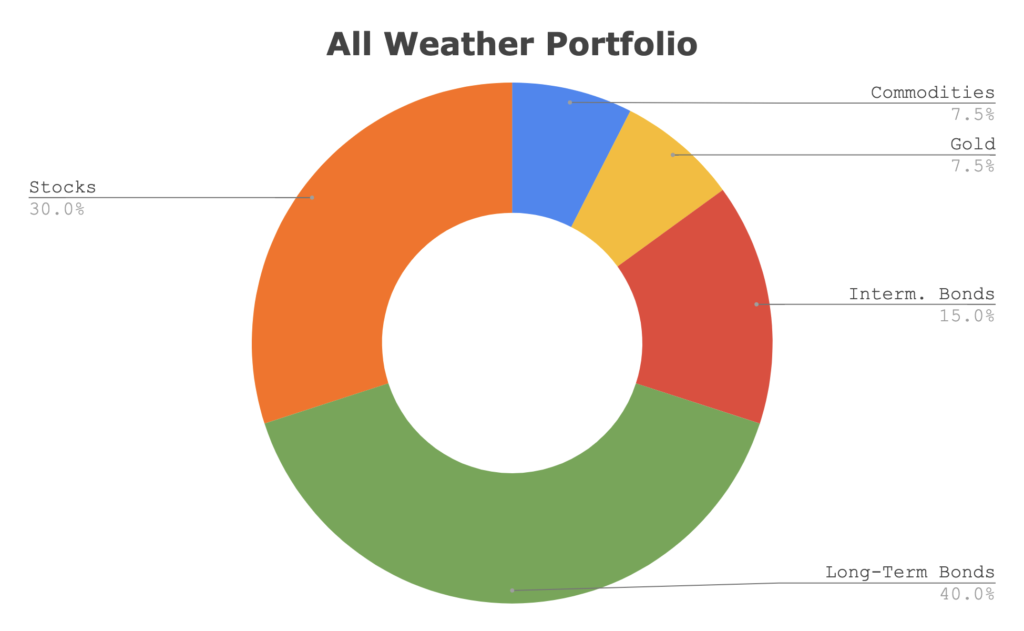
Based on back-testing, essentially Dalio and his Bridgewater team came up with a model after studying the relationship between asset class performance and changing market environments. The result of this relationship crystallized the following asset class allocation that would investors to benefit whether the market is moving up or down or sideways.
Here is the asset class breakdown:
We’ll provide more detailed funds to mimic this portfolio in a bit.
One thing you’ll realize from the portfolio above is the all-weather portfolio takes a much different approach than age-based allocations (i.e., more bonds as you get older in your portfolio), the traditional 60/40 balanced portfolio, or other popular couch potato approaches. It essentially ignores an investor’s personal need for changing risk appetite. A drawback we’ll discuss more in a bit.
The theory of the All-Weather Portfolio is that:
- The equity portion will thrive in bull markets.
- Commodities and gold should support the portfolio for inflation.
- Bonds will help investors when stock market growth is suffering…
You get the idea. Continue Reading…