Special to the Financial Independence Hub
We often think of wealth building and retirement as static dates. We have that accumulation stage when we are building our assets and net worth, and then we have that decumulation stage (retirement or semi retirement) when we are spending our assets. We tend to think of those periods in static terms, with hard stop and start dates. But that could be dangerous thinking thanks to what Dr. Moshe Milevsky of York University describes as the Retirement Risk Zone. That period is typically 5 years before your retirement date and the first 5 years of retirement. That is when the risks are greatest for a retiree.
We need to prepare our investment portfolios well in advance of our planned retirement date. We need to protect our ASSets. And certainly we build wealth in many ways or by many channels. We have our cash and investment portfolios, and we may also have workplace pensions that are building future retirement payments. And of course we have our real estate and perhaps we are also building value and net worth in business ventures. We may have inheritances that we know are likely to come our way. On that front, we don’t want to count those chickens before they hatch.
In this post we’ll discuss protecting the assets that potentially hold the greatest risk: the stocks in your investment portfolios. Of course the funds could be in an RRSP, RRIF, a locked-in plan of sorts, your TFSA or in taxable accounts. And the risk comes from holding those stocks that can be more than volatile at times.
As a refresher, imagine if you had picked January 2008 as your retirement date. In 2007 things are looking rosy and then the Financial Crisis hits and the US stock markets fall by more than 50%. The chart is courtesy of portfoliovisualizer.com
 Your handsome $350,000 RRSP portfolio gets clipped to fall below $200,000. If a retiree was spending down in typical fashion on the above portfolio they would have seen that $350,000 drop to the $170,000 range. If one entered retirement with an aggressive all-stock stance, they might have their retirement permanently impaired. The Retirement Risk Zone is more about the retirement funding math compared to your tolerance for risk.
Your handsome $350,000 RRSP portfolio gets clipped to fall below $200,000. If a retiree was spending down in typical fashion on the above portfolio they would have seen that $350,000 drop to the $170,000 range. If one entered retirement with an aggressive all-stock stance, they might have their retirement permanently impaired. The Retirement Risk Zone is more about the retirement funding math compared to your tolerance for risk.
Related post: How Retirees Made It Through The Last Two Recessions
When should you prepare your portfolio for retirement?
Again, Dr. Milevsky suggests the risks are great even 5 years before retirement. I’ll give an example using perhaps the most dangerous start date for a retiree over the last 50 years: the year 2000. This was the beginning of a stock market correction that simply would not let up. US stocks were down for 3 successive years in 2000, 2001 and 2002. That has only happened twice in US stock market history, you’ll have to go back to the Great Depression of the 1920s and 1930s to find the other event. Canadian stocks were down for 2 years in a row and did not suffer the same level of meltdown (though it was certainly a troubling bear market).
As you can imagine if a retiree had the year 2000 as a retirement start date and they entered retirement with an all stock portfolio that asset bucket would have been permanently impaired. Of course, I’m assuming that they need to spend from that account type. If you need to spend from that plan or retirement bucket, you need to protect those assets at least 5 years in advance.
Here’s an example of failure in the last years of portfolio accumulation for a retiree. The year is 1998, the stock markets are one the greatest kicks in stock market history and our retiree is smiling from ear to ear with those incredible portfolio gains and a planned 2003 retirement date.
In 1998 our future retiree has $350,000 in her RRSP account, she is still adding $700 monthly, or $8,400 annual. Once again, we’ll use the US stock market for demonstration purposes. Of course you hold a more diversified asset mix.
 The retiree has been adding monies on a regular schedule for 5 years and has a negative rate of return. The real rate of return when we factor in inflation is even less favourable. The retiree started 1998 with $350,000, added $42,000 and ended the period with just over $369,000.
The retiree has been adding monies on a regular schedule for 5 years and has a negative rate of return. The real rate of return when we factor in inflation is even less favourable. The retiree started 1998 with $350,000, added $42,000 and ended the period with just over $369,000.
In Scenario 2 our retiree moves to a Balanced Growth model in 1998. She is now 70% stocks and 30% bonds (I’ve used 10 year treasuries). She enters 2003 with modest but positive returns for the period, and with a portfolio value of $438,000.
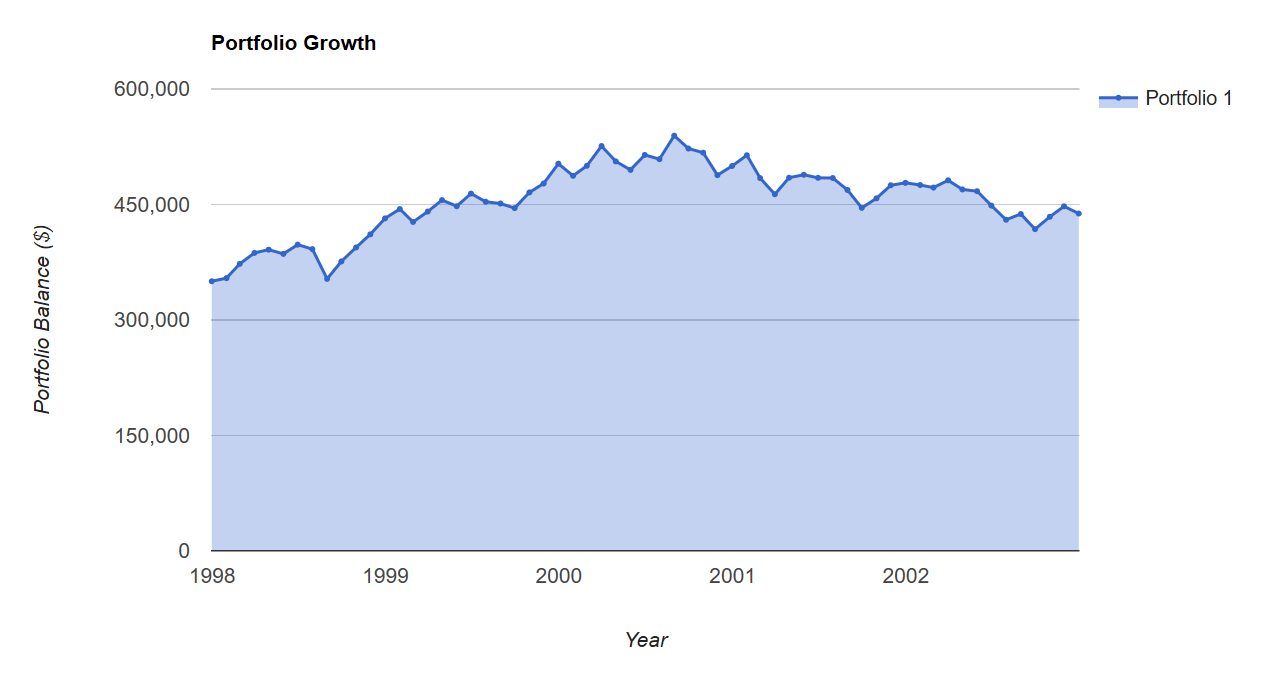 And of course, to a point, the more conservative a portfolio (more bonds) the better for the test. But hey, that’s all certainly hindsight as we’ve picked the worst possible retirement start date. Right? Not so fast. Even if we look at the 2008 market correction protecting the assets well in advance works much better, and the more conservative the balanced portfolio, the better. You might at least keep your equity allocation in the 30%-40% area.
And of course, to a point, the more conservative a portfolio (more bonds) the better for the test. But hey, that’s all certainly hindsight as we’ve picked the worst possible retirement start date. Right? Not so fast. Even if we look at the 2008 market correction protecting the assets well in advance works much better, and the more conservative the balanced portfolio, the better. You might at least keep your equity allocation in the 30%-40% area.
*And certainly, one can use other assets beyond bonds to manage risks.
We are on the same last few years accumulation strategy with a 2010 retirement start date. In this example we are ‘protecting’ the funds 6 years in advance.
Portfolio 1 is all US 100% equity.
Portfolio 2 is 60% stocks and 40% bonds.
Portfolio 3 is 40% stocks and 60% bonds.
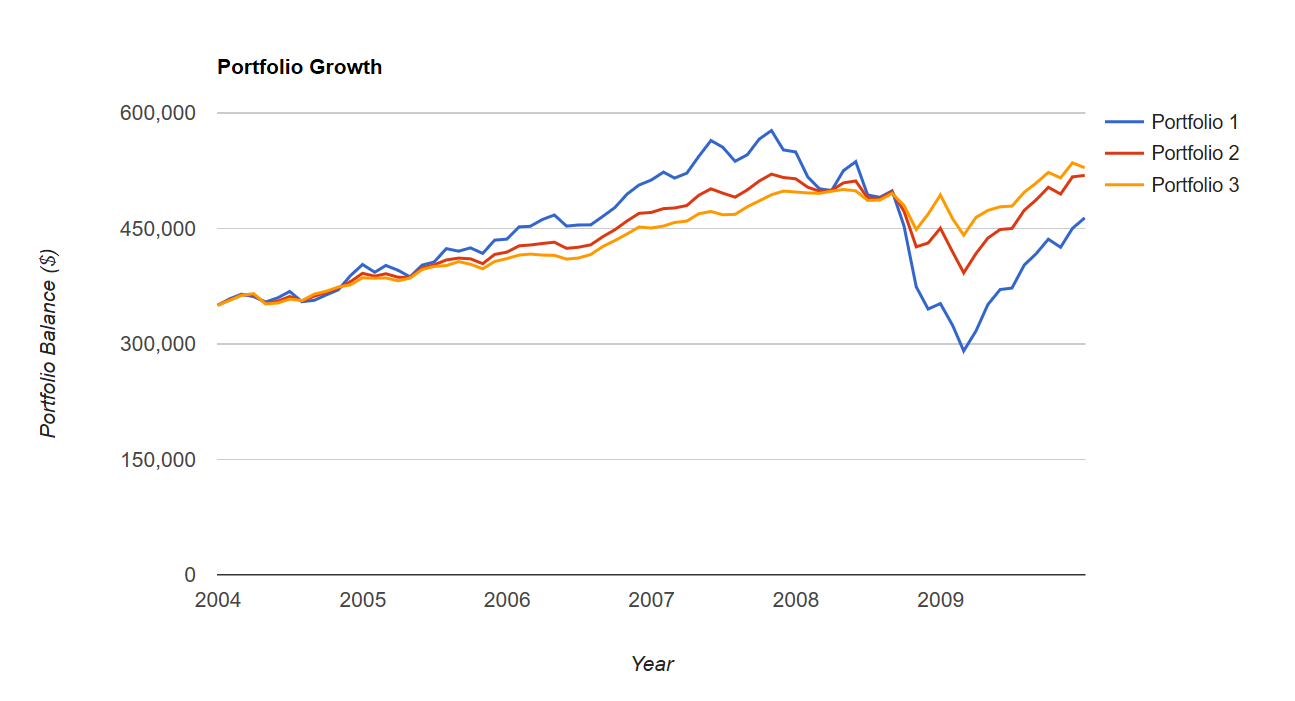 The only time this strategy will fail, that is deliver opportunity cost, is when we take out a severe market correction and invest only in a period of mostly rising markets (bull markets). Of course as an investor or advisor that is not a risk that you want to take. You do not want to guess that a stock market correction is not in the near future. Stock market corrections historically come along with regularity. We are currently in an abnormal period of an extended (mostly) bull market run.
The only time this strategy will fail, that is deliver opportunity cost, is when we take out a severe market correction and invest only in a period of mostly rising markets (bull markets). Of course as an investor or advisor that is not a risk that you want to take. You do not want to guess that a stock market correction is not in the near future. Stock market corrections historically come along with regularity. We are currently in an abnormal period of an extended (mostly) bull market run.
A more conservative accumulation stage
As we approach the final turn toward the retirement ‘finish line’ we obviously want to increase our portfolio value.
The key will be to invest with a more conservative approach in the last several years. If one is aggressive and has the risk tolerance level, they may choose a Balanced Growth Model. That appears to be the sweet spot for risk-adjusted returns and also for optimal portfolio income in retirement. Please have a read of The Balanced Growth Portfolio. The Investor’s Sweet Spot. You’ll see the Balanced Growth Model can typically keep pace with an all-equity model thanks to those market corrections.
How to adjust the One Ticket Asset Allocation Portfolio approach
Here’s a great post from John Robertson, the author of The Value of Simple. Of the course One Ticket Portfolios are very popular for many, very good reasons. Investors can access complete managed portfolios with MERs in the range of .25%. Here’s John’s All-in-one ETFs and changing asset allocation. There are many great tips in that post with regards to taxable accounts. Most notably, you can likely avoid any tax hit by planning in advance. If you are a self-directed investor you can simply add a bond component to your mix, over time. If you do want to sell from an all-equity One Ticket Portfolio and move to a balanced model you can spread the tax hit over a few years. Of course, there are no rebalancing tax implications for registered TFSA, RRSP and RRIF etc.
Related post: Which Vanguard All-In-One, One Ticket Portfolio Should You Invest In?
Once again, that’s why it is important to be well aware of the risks well before our retirement date, and to make the appropriate moves well in advance to avoid unnecessary fees and taxation.
Checking in with advice-only financial planners
As I often write, preparing for retirement and managing your income streams in the most effective manner in retirement can be tricky business. If your scenario is in any way ‘complicated’ you may want to touch base with an advice-only planner. They can help in many ways, including with taxation, estate planning and allowing you to see the most effective order of asset harvesting. That can be a changing and shifting puzzle. You may lean heavily on your RRIF early in retirement, and then mostly let it run for a few years. Your need to protect equity assets can ebb and flow in concert.
Advice only planner Nick Hui of Vave Financial prefers a very conservative approach. From Twitter, I’m @67_Dodge.
I wouldn’t even recommend a 100% stock exposure in their 40s (age). Probably balancing out their asset allocation slowly from age 40 to 60.
Jason Heath of Objective Financial Partners suggested that it ‘all depends’ as it is a difficult question to answer given that each situation (retiree) is more than unique. That said, Jason did suggest that when a stock asset needs to be protected he will begin about 5 years or more in advance of that ‘asset need’ date.
 A key part in that post, once again, is that reference to decumulation sequence.
A key part in that post, once again, is that reference to decumulation sequence.
Do you have a retirement plan?
We need to do more than save and invest for retirement. We need to plan well in advance. That includes getting your monies in the right ‘buckets’ and protecting those assets well in advance. Questions to me, Dale @cutthecrapinvesting@gmail.com. Or better yet, leave a message on this post.
Thanks for reading. Kindly hit those share buttons for Twitter, Facebook and LinkedIn. You can Follow Cut The Crap Investing at the very bottom of this page.
 Dale Roberts is the Chief Disruptor at cutthecrapinvesting.com. A former ad guy and investment advisor, Dale now helps Canadians say goodbye to paying some of the highest investment fees in the world. This blog originally appeared on Dale’s site on May 30, 2019 and is republished on the Hub with his permission.
Dale Roberts is the Chief Disruptor at cutthecrapinvesting.com. A former ad guy and investment advisor, Dale now helps Canadians say goodbye to paying some of the highest investment fees in the world. This blog originally appeared on Dale’s site on May 30, 2019 and is republished on the Hub with his permission.



