My latest MoneySense Retired Money column has just been published. You can find it by clicking on the highlighted text here: Why “unretirement” may be the fate of so many Canadians.
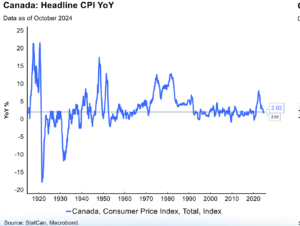
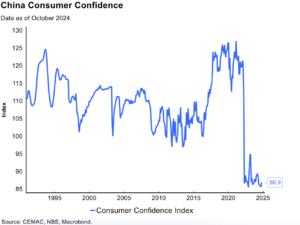
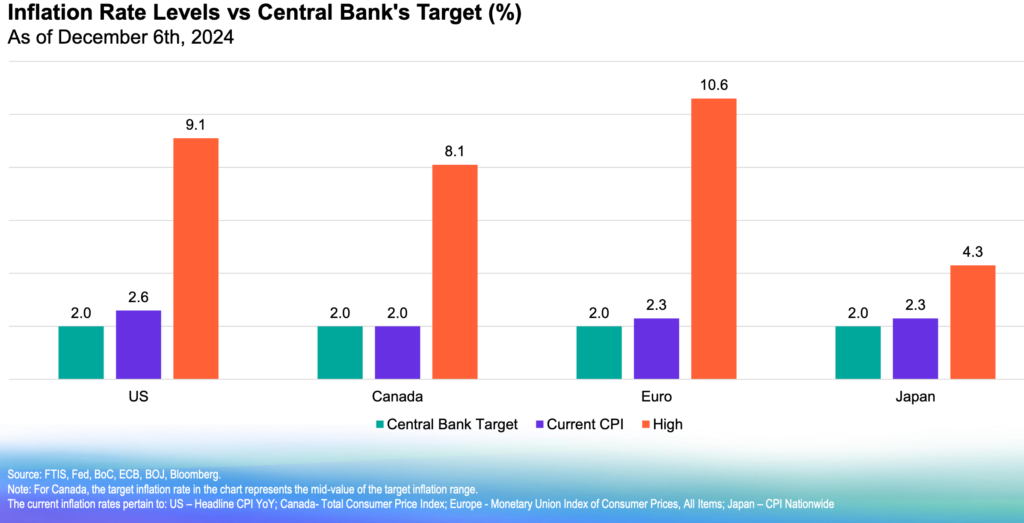
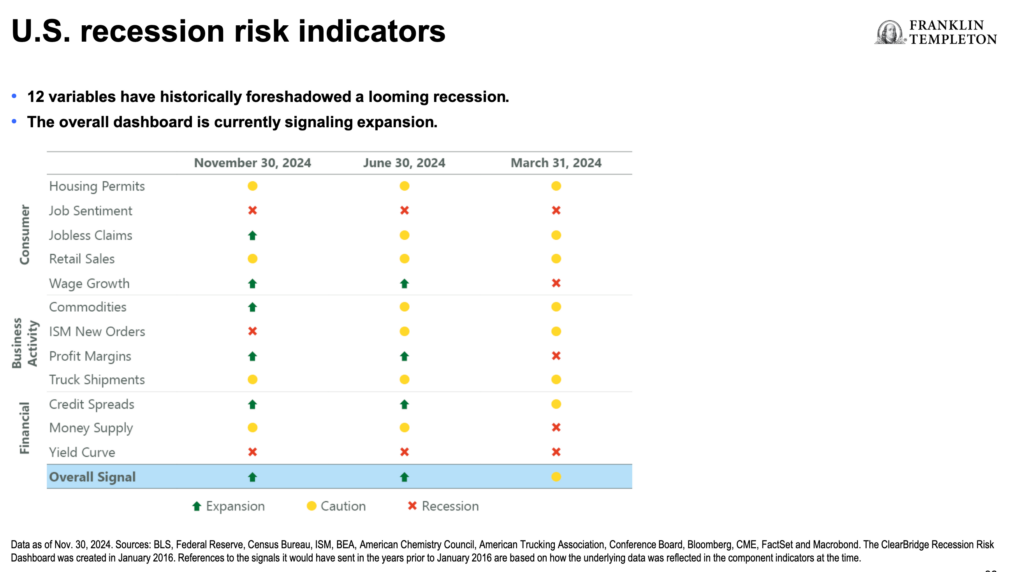
Even before the Tariffs threats emerged under Trump 2.0, Canadian seniors were starting to find the economic uncertainty and rising living costs to be unmanageable. No surprise then that many seniors approaching Retirement Age are delaying their exit from the workforce.
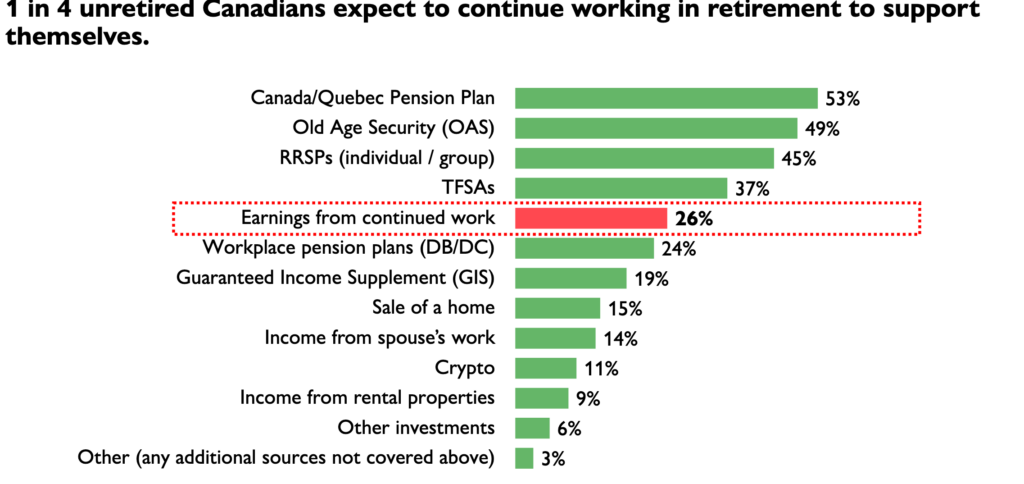
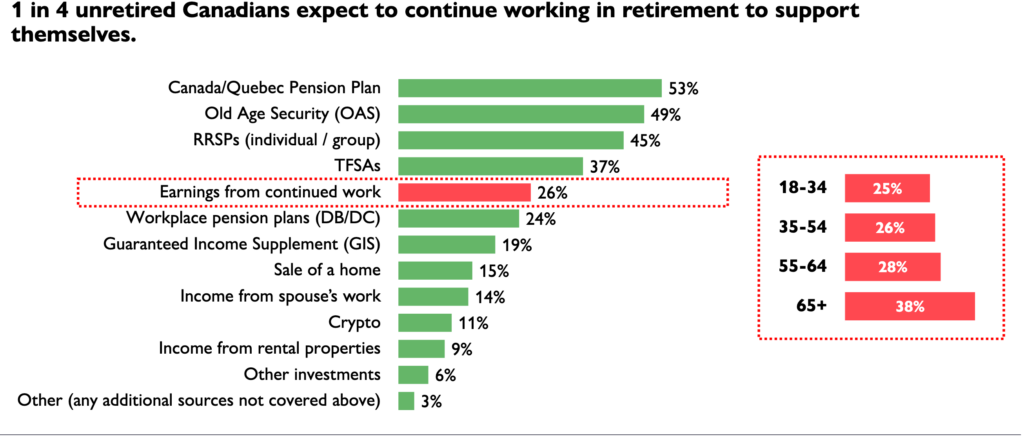
According to a report by HealthCare of Ontario Pension Plan, 28% of unretired Canadians aged 55-64 say they expect to continue working in retirement to support themselves financially. Here’s a screenshot from the HOOPP survey:
The Healthcare of Ontario Pension Plan (HOOPP) commissioned Abacus Data to conduct its sixth annual Canadian Retirement Survey in the spring of 2024. The latest survey finds “persistent high interest rates and a rising cost of living continue to have a significant negative impact on Canadians’ ability to save and manage the cost of daily life, threatening their retirement preparedness.” While all Canadians are struggling, “women and those closest to retirement are especially hard hit with lower savings and higher levels of financial stress.”
While most Canadians are struggling to save amidst a high cost of living, HOOPP finds women are particularly affected. Half (49%) of all Canadian women have less than $5,000 in savings and almost a third (28%) have no savings (compared to 33% and 17% of men, respectively), similar to the 2023 results
The MoneySense column also looks at more recent Retirement surveys that also reveal anxiety about rising costs of living. One is from Bloom Finance Co. Ltd., conducted by founder Ben McCabe after Trump’s Tariffs started to kick in this year.
A Bloom study conducted with Angus Reid found 46% of Canadians thinking of working part-time in Retirement. That’s in line with a Fidelity survey in 2024 that found half of Canadians plan to delay Retirement. According to the Bloom Report [in March 2024], 67% of Canadian homeowners over 55 were concerned their savings would not sustain their quality of life through retirement. Only 29% considered downsizing or alternative living situations to access their home equity earlier than expected. 59% of the same cohort agreed accessing micro-amounts of their home’s equity would help maintain their desired living standard. Continue Reading…