My latest MoneySense Retired Money column looks at a variety of tax and savings limits changes that are effective early in 2025. Click on the highlighted headline for the full column: What retirees need to know about tax brackets for 2025.
As the column notes, at or near Retirement taxes and inflation are the two big threats to preserving enough wealth to last a lifetime. The tax burden hits home with the annual tax-filing deadline in April, but the time to start thinking about the yearly ordeal is before year-end.
The complexity of this task is compounded by almost-annual changes to tax brackets, the Basic Personal Amount, OAS thresholds, inflation adjustments and much more. For starters, I recommend reading an excellent article by CIBC Wealth’s tax guru, Jamie Golombek, which appeared in the Financial Post here on Nov. 23rd, shortly after the Canada Revenue Agency released its new tax numbers for the year 2025.
Let’s look first at inflation, the second serious scourge retirees face if they live long enough. Here, a useful tool suggested by certified financial planner Morgan Ulmer is Statistics Canada’s Personal Inflation Calculator, which lets you compare your personal inflation rate to the general CPI.
Ulmer, of Toronto-based Caring for Clients, sees the higher tax brackets and inflation adjustments as an “opportunity for retirees to build a savings reserve.” CPP is indexed to inflation yearly while OAS is indexed quarterly. So “if a retiree is able to increase their spending at a rate that is less than CPI, the difference could be saved as an emergency reserve or invested in a TFSA.”
Inflation and Tax Bracket changes
Back to some key data cited by Jamie Golombek. The inflation rate used to index 2025 tax brackets and amounts will be 2.7%: just over half the 4.7% in effect in 2024. The good news is that the Basic Personal Amount (BPA) on which no federal tax is levied rises to $16,129 in 2025: It was $15,000 in 2023.
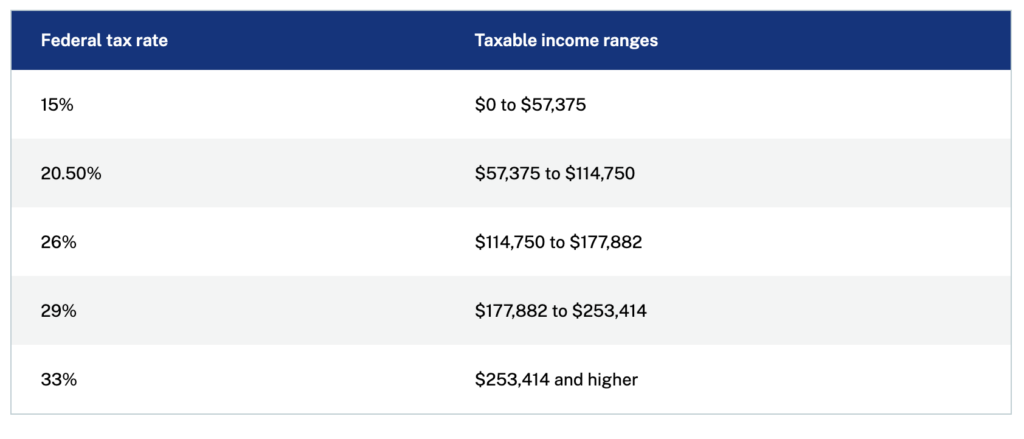
All five federal income tax brackets are indexed to that 2.7% inflation rate. In 2025, the bottom federal tax bracket of 15% will apply to incomes between zero and $57,375. The second lowest bracket of 20.5% will apply to incomes between $57,375 and $114,750. The 26% bracket applies to income between $114,750 and $177,882, while incomes between $177,882 and $253,414 will attract a 29% federal tax. After that the federal rate will kick in at 33%.
Below is a table summarizing that information prepared for MoneySense:
Don’t forget there will be additional provincial taxes on top of the federal haul, also indexed to inflation at various provincial rates.
What is relevant for those in the Retirement zone is the higher threshold on Old Age Security: in 2025, according to Canada.ca, OAS begins to get clawed back for taxable income of $90,997. OAS benefits disappear entirely at $148,451 for those aged 65-74 in 2025, and at $154,196 for those 75 or over. Note the OAS clawback is based on individual incomes, not household income.
Deferring CPP and OAS till 70
Matthew Ardrey, portfolio manager and Senior Financial Planner for Toronto-based TriDelta Financial, agrees that tax brackets, whether federal or provincial, “become more of a consideration in retirement.” For many Canadians receiving employment income on a T-4, there is little we can do as retirees to keep income in the lower tax brackets. But there’s plenty to think about when considering tax minimization and decumulation strategies. Referring to Golombek’s article, Ardrey says that using federal brackets only, taxpayers can receive $57,375 of income and pay very low rates of taxation, especially when the $16,129 basic personal amount is considered.”
Retirees under age 70 can defer CPP and OAS until 70 and try to live on withdrawals from their registered plans instead. With no other income, taxpayers could have almost $50,000 of after-tax income, or $100,000 for tax-paying couples. Continue Reading…





