With so many Canadians plugged into the latest Trump Tariff news, I felt that I needed to get an updated trade war column out as soon as possible!
So what I’m going to do today is update an article I wrote back when we were taking our first baby steps into Trump Tariff reality. Below you’ll see a ton of info on what tariffs are, what Canada’s situation is in regards to the big picture effect on our economy, and finally, what the impact is likely to be on your portfolio.
But first, just to bring you up to speed, here’s what the President announced in his big “Liberation Day” speech – complete with grade-five-science-fair-style cardboard visual aid.
- A baseline tariff of 10% will be imposed on nearly all imported goods from all countries. This tariff is set to take effect on April 5, 2025
- Canada and Mexico will not – for the moment – be part of that 10% baseline tariff.
- Canada and Mexico trade is basically now broken up into three categories: goods that are USMCA-compliant, goods that are not UMSCA-compliant, and goods that are in sectors that Trump wants special rules for.
- USMCA-compliant goods are actually in the best spot of any imported goods in the world right now – as they get to enter the USA tariff-free!
- Goods that are not UMSCA compliant are still under the 25% “Fentanyl Tariff” rules.
- We already knew about potash and fossil fuels having their own 10% tariff rules, but it appears that lumber, steel, and aluminium will continue to have their own special place on the Trump Tariff list as well.
- Likely the biggest Canada-related news was that the 25% tariff on automobiles will be applied to Canadian-made vehicles (despite the USMCA explicitly outlining this as being illegal).
In regards to the rest of the world, the most noteworthy developments were:
- An additional 34% tariff on China, resulting in a total tariff of 54% when combined with existing duties.
- European Union: A 20% tariff.
- Japan and South Korea: 25% and 24% tariff respectively.
- India: 26% tariff.
- Vietnam: 46% tariff.
- Many many many other tariffs.
As we hit publish on this article, countries around the world were announcing retaliatory tariffs and US stock market futures were showing that the overall US stock market was set to lose 4% as it opened on April 3rd.
The best quote that I heard in regards to summing up this whole mess was from Flavio Volpe, president of the Automotive Parts Manufacturers’ Association who stated that the new tariff situation was “like dodging a bullet into the path of a tank.” He went on to write, “The. Auto. Tariff. Package. Will. Shut. Down. The. Auto. Sector. In. The. USA. And. In. Canada,” and then, “Don’t be distracted. 25% tariffs are 4 times the 6/7% profit margins of all the companies. Math, not art.”
It appears that the rest of the world is finally waking up to the same reality that Canada and Mexico have been experiencing for the last two months. There’s much more that could be written about the gnashing of teeth and simply incredible quotes from the President such as, “An old-fashioned term that we use, groceries. I used it on the campaign. It’s such an old-fashioned term, but a beautiful term: groceries. It sort of says a bag with different things in it.”
Oooook.
For now, take a deep breath and read what I had to say a month ago in regards to your stock portfolio. The reality was true then, and it’s true today. In my predictions column back in late December I wrote:
“One of the most pressing questions for Canadian businesses in 2025 is whether the newly elected U.S. president will follow through on his promises of large tariffs on Canadian imports.
Trump’s fixation on trade deficits could lead to a significant shake-up in the global economy. He appears intent on generating tariff income to support the legislative groundwork for corporate tax cuts. His “national security” justification may lack substance, but it could still trigger sweeping trade policies.
I don’t actually believe that Mr. Trump understands how trade wars actually work, and he hasn’t cared to learn anything new in several decades. So the hopes better angels will talk him out of this are perhaps misplaced.
I believe even more strongly that the President-elect doesn’t understand how trade balances work, and consequently, he does not understand that in buying goods from Canada with a strong US Dollar, his constituents (US consumers) are winning! There is no “subsidization” of Canadian business going on here.
While a blanket 25% tariff on all Canadian goods seems unlikely, a more targeted 10-15% tariff on non-energy products feels probable. If that happens, Canadian businesses would face a challenging environment, and retaliatory tariffs from Canada could escalate tensions further.
My guess is that we’ll see some major disruption in Canadian manufacturing, with supply chains snarled, and some factory commitments being delayed indefinitely as companies decide to move more operations within the USA for the next few years at the very least. I’d also be pretty worried if I was a farmer and/or worked in the dairy industry. Some of these tariffs might come off when the overall North American trade deal is finalized.”
I’d say that held up pretty well!
The key here is definitely not to panic. The Canadian stock market has actually held up pretty well so far – and as always, it’s key to remember that the vast majority of the companies in Canada’s stock market DO NOT depend on selling specific goods to the USA. It’s also worth noting that a lot of companies that weren’t previously UMSCA-compliant are likely to become so in a hurry. If that happens, there might actually be a lot of Canadian companies in an enviable position relative to the rest of their global competitors as they will have no tariff to worry about (for now) versus 10%-50%+ for other countries.
This isn’t going to be good for any of the world’s economies, but the Trump Tariffs are already proving very unpopular with US Citizens and even among Republican politicians. Read on for more detailed reasoning on why you don’t need to do anything drastic in the face of these latest Trump tariff developments, and the broader US – Canada Trade War that has now expanded to include the rest of the world.
Trump (Delayed) Tariff Details
So – what is a tariff anyway?
A tariff is a tax by a government on foreign goods coming into a country. The import company (or person) pays the tax to the US federal government. In the vast majority of cases, the company then turns around and sells the imported product for a higher price (and possibly also takes a hit to their profit margin).
Trump’s tariff summary:
- A 25% tax on all imports – aside from oil. This happens on Tuesday, February 5th.
- A 10% tax on oil. This is supposed to kick in on February 18th.
- Mexico will see a 25% tax on all of its imports.
- China will get a comparatively light 10% tariff on its imports.
- Canada will respond with two-phases of tariffs in response. They will total $155 billion of US goods.
- Mexico hasn’t finalized details but announced tariffs ranging from 5% to 20% on US imports including pork, cheese, fresh produce, manufactured steel and aluminum.
If you’re wondering what we send to the USA – it’s a lot (we don’t have 2024 numbers finalized yet).
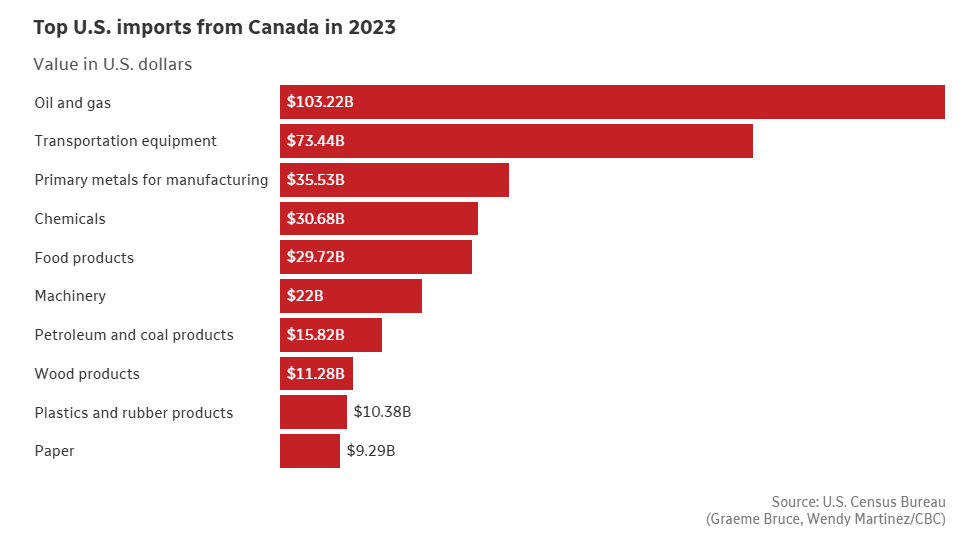
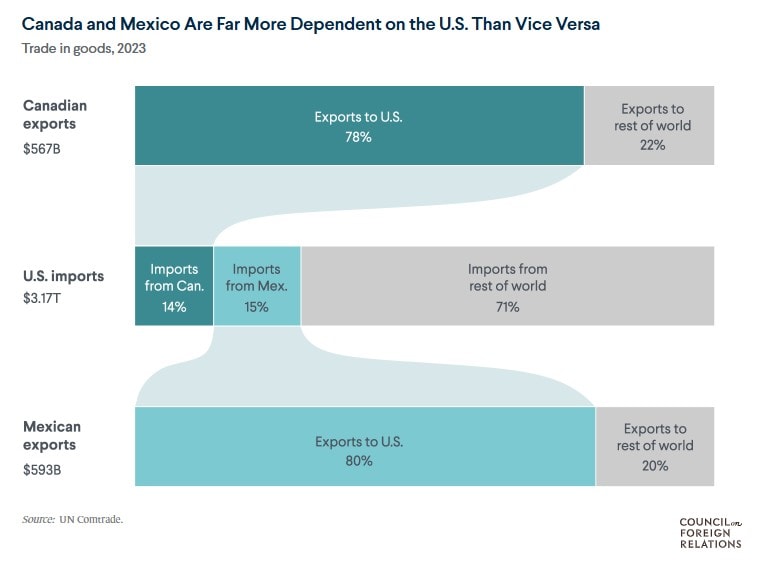
The potential fallout from U.S. tariffs looms large. If the worst-case scenario unfolds and these tariffs stay on Canadian companies for more than a month or two, economists estimate it could push Canada into a three-year recession, shave three percentage points off our GDP, and wipe out 1.5 million jobs. While forecasts vary, one thing is clear – the economic risks are significant. It would likely be even worse for Mexico.
The USA isn’t going to get off the hook easily either. Predictions range between their GDP shrinking .3% to 1%. That range doesn’t give a precise picture of the fact that counter-tariffs will be heavily targeted with the goal of inflicting maximum pain to companies that are important to Republicans’ electoral chances. I wouldn’t want to be in the US alcohol or consumer goods business right now.
American consumers are going to immediately see higher prices on agricultural goods, lumber (which means more expensive houses), gasoline (especially in the midwest), and vehicles.
When it comes to cars, the idea that the tariffs will somehow shutdown Canadian factories and move them to the USA overnight is ridiculous. What will happen is that the complex supply chains involved for North American manufacturers will get much more expensive, and consequently it will make the final product more expensive. Continue Reading…









