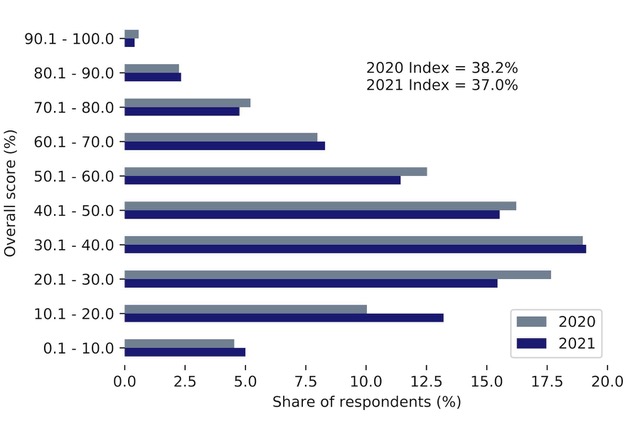
Financial knowledge about the Canadian retirement system fell from 2020 to 2021, says the Retirement Savings Institute.
The financial literacy of average Canadians is still low when it comes to understanding our Retirement system, says a survey being released Tuesday. The third edition of the Retirement Savings Institute (RSI) surveyed 3,002 Canadians aged 35 to 54 and found the overall RSI index measuring knowledge of the retirement income system slipped from 38% in 2020 to 37% in 2021. This, it says, is “still showing a significant lack of knowledge among Canadians.”
The RSI Index is the share (stated as a percentage) of correct answers to 29 questions posed in the survey.
The best-understood subjects continue to be CPP/QPP and RRSPs/TFSAs. Canadians still find it tougher to understand employer sponsored pension plans and Old Age Security, where the average respondents “didn’t know” the answer to half the questions.
In a backgrounder, the RSI team at HEC Montreal [a business school] says the scientific literature in several countries has established a link between general financial literacy and preparation for Retirement. However, “the level of general financial literacy among Canadians is fairly low, although comparable to what is observed elsewhere in industrialized countries.” It also finds knowlege about narrower topics like taxes to be “rather limited.”
Starting in 2018, the RSI started to measure on an annual basis the financial literacy of Canadians in their “years of strong asset accumulation in preparation for retirement.” Those younger than 35 tend to have “other concerns and financial priorities than retirement,” the RSI says.
Knowledge rises with education and income, and as retirement nears
Not surprisingly, the closer to Retirement age one is, the more knowledgeable of related financial matters we tend to become. The RSI score was 33.9% for the youngest in the survey aged 35 to 39, rising to 36.6% for the 40 to 44 cohort, then to 37.8% for the 45-49 group, and a high of 39.5% for those 50 to 54.
Also as one would expect, the more schooling the higher the score: those with high school or less had an RSI score of 31.5%, while those with college or equivalent scored 36.9%, and those with a Bachelor’s degree or higher scored on average 45.3%. Similarly, the higher the household income, the better knowledge. Thus, those with household income of $30,000 or less scored just 26.1%, compared to $60,000 to $90,000 families scoring 37.3% and at the highest, families making $120,000 or more scored 45.6%.
Equally unsurprising is the fact that higher earners are more knowledgeable about RRSPs and TFSAs, especially when it comes to contribution room and withdrawal rules. They are less knowledgeable about investment returns in those vehicles, and score a low 12.6% on penalties for over contributions and other rules related to taxes.
Many confused about Employer Pensions
Employer pension plans seems to be an issue. At all ages, Canadians found it difficult to know the difference between Defined Benefit (DB) and Defined Contribution (DC) pension plans. In particular, they tend to be confused about which one reduces longevity risk (DB) and which depends on returns generated by financial markets (DC). Low-income individuals are even less knowledgeable.
Workers who are contributing employer pension plans had significantly higher scores (41%) than those who were not enrolled in such plans (32.9%).
The older and richer understand CPP/QPP better
Also as you’d expect, older people and more well-off people understand the Canada Pension Plan (CPP) or the Quebec Pension Plan (QPP) better. As the chart below illustrates, most Canadians are now well aware that taking early CPP/QPP benefits results in lower monthly benefits (shown in the “Penalty” bar), but there is still a lot of confusion about whether CPP/QPP recipients can collect benefits while still working (only 25% correctly answer this.)
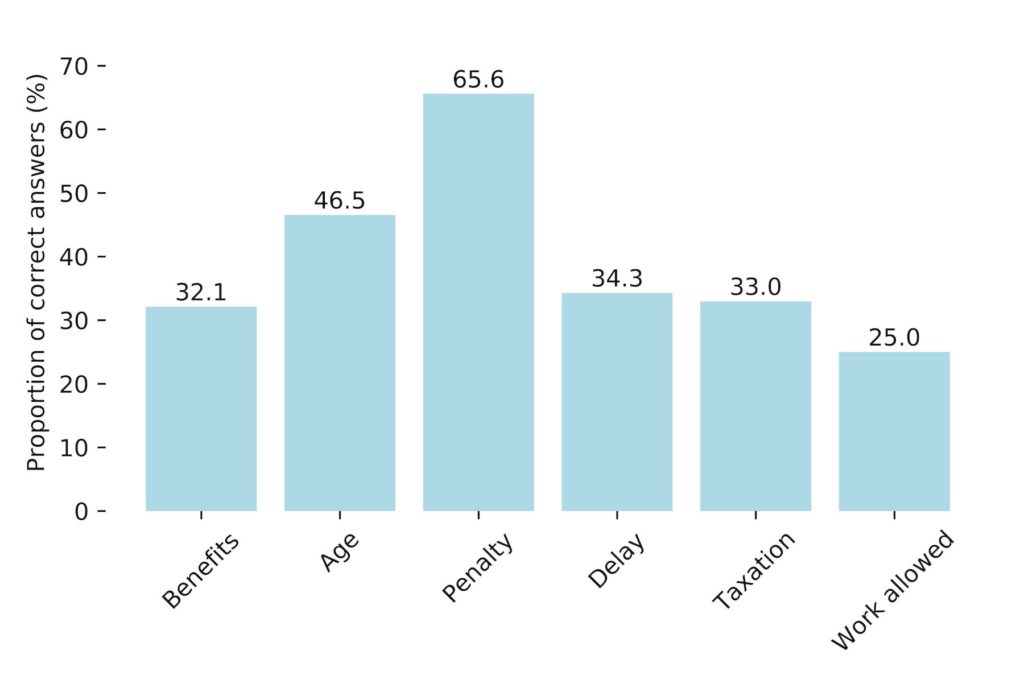
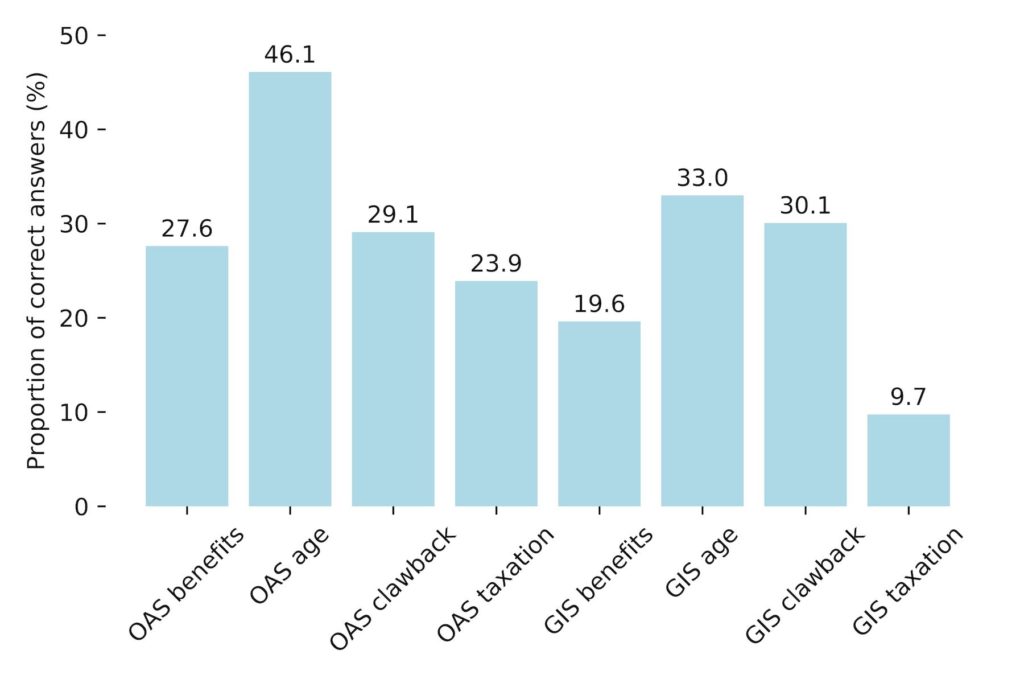
Older people also know OAS and GIS better. As the chart below shows, most people know you have to be at least 65 years old to receive OAS, but knowledge about technical matters like the OAS clawback, the Guaranteed Income Supplement to the OAS, and taxation of these benefits tends to be much scantier.
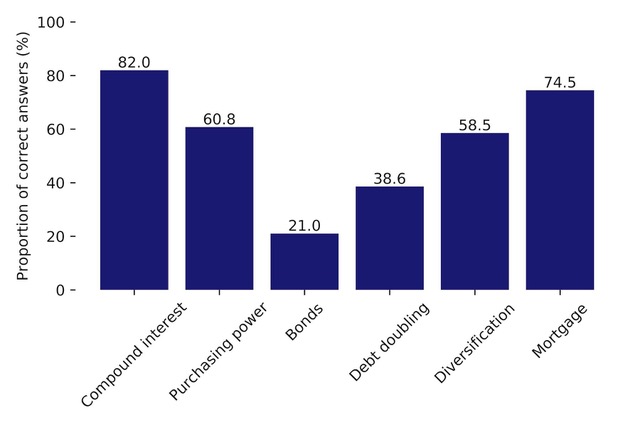
Mortgages well understood, bonds and debt not so much
When it comes to major financial products, Canadians are quite knowledgeable about compound interest, but as less so about debt doubling and quite ill-informed about Bonds, as the chart below indicates. (
Debt doubling suppose a $1,000 loan with interest charged at 20% per year — typical of credit cards –and the question posed was how many years it would take for the debt to double if no interest were paid off.)
All in all, an interesting analysis of financial literacy during a period when it really starts to have an impact on one’s personal finances: the late wealth accumulation years up to the pre-retirement income preparation time.


