By Matthew Marchand
Special to Financial Independence Hub
More Canadian businesses are failing this year.
In the second quarter of 2023, the Canadian Association of Insolvency and Restructuring Professionals (CAIRP) noted that there were 1,090 business insolvencies — an increase of 36.9% compared to the same period in last year. It was also the highest volume since 2014.
There are two main reasons why this is occurring.
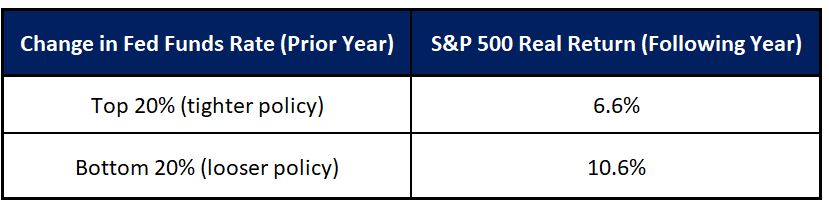
First, the combination of rising interest rates and high debt levels has resulted in slower consumer demand and increased debt servicing costs for both businesses and consumers. The prime rate has risen 475 basis points since early 2022 and now sits at 7.2%.
Second, the loss of government financial aid plus the need to repay a portion of the aid received — along with tightening credit conditions — are making it more challenging to obtain new financing or to refinance existing debt.
During the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, government financial aid helped limit insolvencies during those challenging times. What we’re seeing now is a normalization after an abnormal period.
It should also be noted that many businesses were beginning to experience financial difficulties prior to the pandemic and the financial aid acted as a buoy to some degree. We’ve seen many instances of businesses being unprofitable prior to the pandemic that became profitable during the pandemic, with much or all the profits being derived from government financial aid.
Now that the financial aid is no longer available and may need to be repaid in the future (depending on the support received), businesses are feeling the challenges of this economic reality.
Ways businesses can survive
Many businesses may think a wind-down of operations is the only option, but that’s not the case. In fact, there are other options:
- A restructuring or compromise of debt (payments to creditors accepted as a settlement of the debts)
- Turnaround initiatives, such as lease disclaimers, labour force reductions or the sale of non-core assets
For businesses that are facing financial challenges now, they should expect interest rates will remain elevated for the foreseeable future. While the Bank of Canada left the overnight rate unchanged at 5% in September, it says it “remains concerned about the persistence of underlying inflationary pressures, and is prepared to increase the policy interest rate further if needed.”
Your organization should update its business plans and financial projections accordingly. If your business doesn’t have a detailed cash flow projection, make one.
You should also conduct a stress test on your financial projections to determine potential financial scenarios and what proactive efforts may need to be taken to avoid worst case outcomes. For example, if sales fall 10% or 15%, how will it affect the financial performance of the business? Will the business be able to meet its debt servicing obligations and other critical payments as they become due, and if so, for how long? Continue Reading…