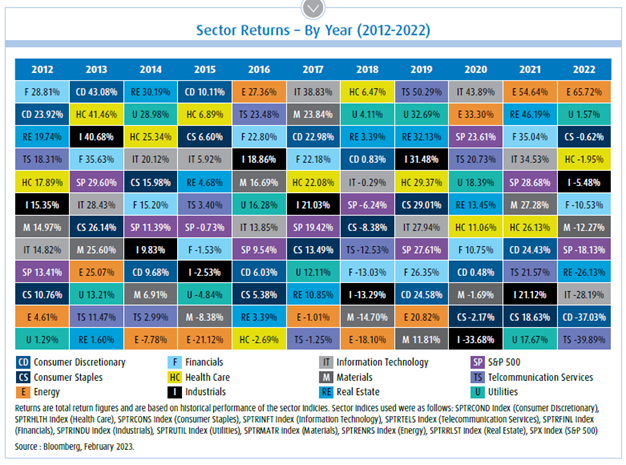
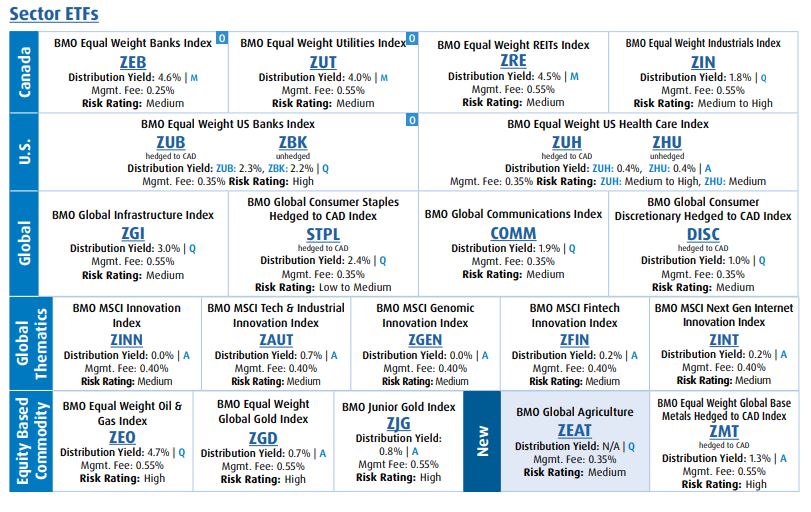
Currency hedging can impact an ETF’s price and overall performance; learn about hedged and unhedged ETFs in Canada here.
By David Kitai, Harvest ETFs
(Sponsor Content)
The idea behind an ETF is relatively simple. At the most basic level, an ETF issuer creates a basket of securities and lists that basket on a stock exchange for investors to buy and sell. The ETF tracks the value of that basket and moves on the market accordingly.
The trouble is, nothing is ever quite so simple. Many Canadian investors want exposure to US securities, as US markets are the largest and most important in the world. What happens when the securities an ETF issuer uses are based in the US, and trade in US dollars, but their ETF will be listed on the TSX and trade in Canadian dollars?
Now, two factors are impacting the ETF: the value of its basket of securities, and the fluctuating exchange rate between USD and CAD. That means, regardless of the value of its holdings, if the USD goes up, the value of the ETF will also go up. If the USD falls, the ETF will also fall. This is called currency risk.
Some ETFs will employ a strategy called currency hedging to minimize the impact of currency risk on an ETF’s value. Those ETFs will usually be described as “Hedged CAD.”
What “Hedged CAD” means
Generally, when an ETF is Hedged to CAD its portfolio managers use a tool called a “currency forward” to lock in a specific exchange rate on a future date. In our Canadian ETF holding US securities example, if the USD has fallen by that date, the ETF makes a gain from the contract which offsets the value it lost from a falling USD on the portfolio holdings. If the USD has risen, the ETF nets a loss from the contract, which also offsets the value it gained from the rising USD.
The goal of currency hedging is not to maximize returns: the goal is to reduce the impact from currency risk as much as possible.
Harvest offers both hedged and unhedged ETFs in its lineup. A select group of Harvest Equity Income ETFs offer a Hedged “A” series and an unhedged “B” series to suit the goals of different investors. You can find a schedule of hedged and unhedged ETFs here.
Hedged vs Unhedged ETFs
So why would some investors want an unhedged ETF? The answer can vary somewhat. Currency hedging also comes with a small cost that is factored into performance over time.
Some investors may buy an unhedged ETF because they want to take on exposure to currency risk. Some investors want to be exposed to certain currencies, and getting currency exposure through an ETF holding foreign securities is one way to achieve that. If an investor believes in the thesis behind a specific ETF, for example the US healthcare sector, and also believes the USD will rise against the Canadian dollar, then buying the unhedged “B” series of the Harvest Healthcare Leaders Income ETF (HHL:TSX) would give them exposure to both a basket of US healthcare stocks and the value of the US dollar against the Canadian dollar. Continue Reading…