By Billy and Akaisha Kaderli, RetireEarlyLifestyle.com
Special to Financial Independence Hub
We at Retire Early Lifestyle like to bring you individual FIRE stories and interviews of interesting people. There is no one single way to retire, and it is our hope that in reading these interviews with those who are on the path to Financial Independence it will inspire you to do the same!
Meet Jon [Jonathan] and Ruth Chevreau
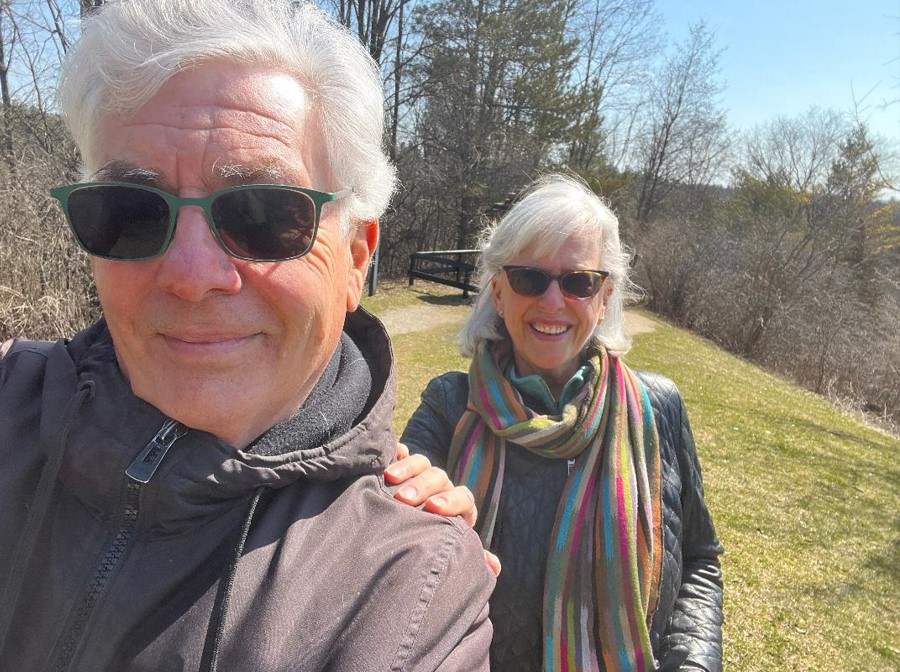

Jonathan (Jon) and Ruth Chevreau
RetireEarlyLifestyle: Could you tell us a little about yourselves? Are you financially independent now?
Jon Chevreau: I’d describe Ruth and me as financially independent, yes, although it’s hard to claim we retired early like yourselves.
I just turned 70 and am still writing and editing, as well as running my own website on Financial Independence. Ruth is a year younger and retired from full-time work when she turned 65. My last full-time employment was at age 61, so by my definition when I became freelance/self-employed that was the start of our Findependence.
But we COULD have left the salaried routine earlier if we had wished to do so: we paid off our mortgage decades ago and our financial assets in combination with small employer pensions and the usual Government pensions are more than enough to fund a modest lifestyle.
REL: What type of work did you do, and what your life was like before FIRE?
JC: I’ve always been a journalist and editor, as well as an author and blogger.
Initially I worked in staff newspaper jobs covering technology in the early 80s ‘for the Globe & Mail (one of Canada’s two national newspapers), then almost two decades covering personal finance and investing for the National Post (Canada’s other national newspaper). I was also editor-in-chief for MoneySense Magazine for a few years after the Post and continue to write and edit for them in addition to running Financial Independence Hub, which I launched in 2014 when I left my full-time job at MoneySense.
REL: Because Billy has a background in finance and securities, he’s very familiar with US investments. Tell us about Canadian-backed assets.
JC: Canada is similar to Australia in its investment profile.
We’re dominated by energy and materials stocks and by six big banks. We have virtually no health care stocks and our consumer staple stocks are really just publicly traded grocery store chains like Loblaw; our tech sector is small. Every once in a while Canada spawns a technology winner: Nortel, which went bust after China’s Huawei “borrowed” some of its technology; Research in Motion, whose Blackberry was a big-time success until the Apple iPhone ursurped it; and currently Shopify is our big tech winner.
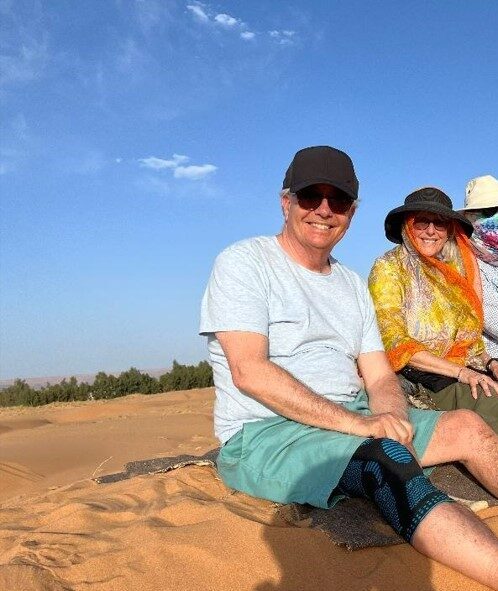

Jon & Ruth sitting on a sand dune in Morocco
But mostly the Toronto Stock Exchange is dominated by banks like Royal Bank, BMO, Bank of Montreal, and TD Canada Trust (all with some US presence) and energy giants like Enbridge and TransCanada Pipelines. An American investor can get away with almost exclusive home country bias since the US is roughly half the global market cap and many of the big players are international anyway.
Canada is maybe 3% of the world’s total market cap, so we are forced to look to the US and global markets to be properly diversified. Once upon a time we were limited to just 20% foreign content in our pensions and retirement plans but that got scrapped so now we can overload on the S&P500 if we wish.
REL: Are discount brokers available to you in Canada like Fidelity, Charles Schwab and Vanguard?
JC: Oh yes, mainly through the big banks, so there’s TD Waterhouse, RBC Direct Investing (both of which we use) and the other banks have similar operations. There are also several independent online brokers like Questrade. Fidelity and Vanguard have Canadian divisions but mostly to sell their mutual funds and ETFs.
REL: Are capital gains taxed more favorably than income in Canada?
JC: Yes. Only half of capital gains are taxed, so that means about half as much tax as is usually paid on interest income or employment income. Also, unlike the US, the capital gains tax in Canada does not rise or fall depending how long you held before taking a profit. Dividends paid by Canadian companies get a lower tax rate than foreign dividends, which are taxed like interest and so best held in tax-sheltered retirement vehicles like the RRSP (Registered Retirement Savings Plan, similar to America’s IRA).

Ruth hiking in Spain
REL: Could you explain Canada’s Old Age Pension, how that works, at what age one can begin receiving it, and how one qualifies for it?
JC: Canada’s equivalent to Social Security is actually three programs we dub CPP/OAS/GIS.
The main one is the Canada Pension Plan, to which all employees must contribute. Like Social Security you can take CPP early (even at age 60) but it pays much more if you wait till 70.
There is also Old Age Security or OAS, which people normally take at the traditional Retirement Age of 65. You can’t get it earlier than that but like CPP, can defer it to 70 and get paid more. It’s funded by the government’s general tax revenues but it’s means-tested, so if you have taxable income above $80,000 or so (the threshold rises a bit each year), you start to have OAS taxed away and you lose it all around $120,000. This is for each person, so retired couples normally try to keep their taxable income below $80,000 each, so $160,000 between them.
Finally, there is the Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS) to the OAS: which is means-tested and aims to top up income for seniors who have no real pensions or retirement savings. Personally, we don’t plan on receiving GIS: most middle-income seniors worry more about preserving OAS benefits: CPP is taxed but benefits are not clawed back.
REL: Could you tell us a little about how your portfolio is structured?
JC: I always used to wonder [in articles] why anyone would need more than a single global balanced mutual fund or these days a comparable Asset Allocation ETF from firms like Vanguard, BlackRock or BMO ETFs.
I believe in diversification by asset class, geography, investment style, and market cap. To some extent I keep in mind the All-Weather Portfolio championed by Ray Dalio, or before that, Harry Browne’s Permanent Portfolio. The latter was 25% in bonds for deflation, 25% stocks for prosperity, 25% gold for inflation and 25% in cash for really bad times. Dalio is a bit like that but would add commodities and maybe real estate. I don’t believe you can consistently predict markets and asset classes so I believe in being exposed to all of these over the long haul, with perhaps shorter-term tactical tweaks if trends become obvious (like interest rates bottoming a year ago.)
REL: How big a part of your retirement plan does the Canadian-based healthcare play? Would you consider permanently relocating to another country? If so, which countries have you considered?
JC: Canadians are a bit spoiled with universal health care. US Democrats would probably call it socialized medicine.
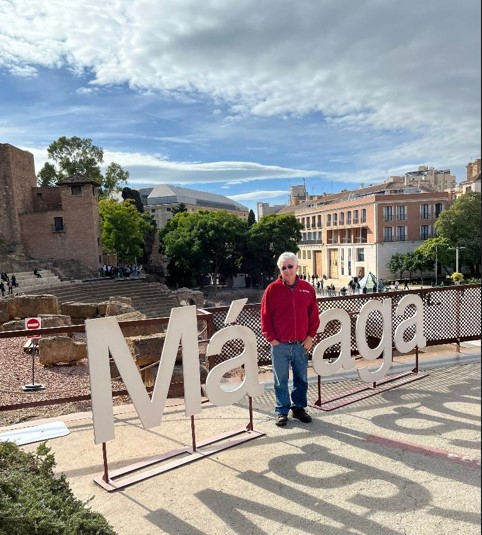

Jon in Malaga, Spain
It’s not entirely free as Ontario levies an annual Health Premium [i.e. tax] depending on income, but it’s lower than private insurance would be. We don’t worry about sticking with a single employer just to keep their health care insurance, although of course some will buy private Blue Cross and that kind of thing beyond what employers provide.
We travel a lot: Florida for a while, more recently Morocco, Mexico and other Spanish-speaking places including Spain itself. But I doubt we’d permanently leave Canada.
Just today we were walking around our home turf by the lake in Toronto. It’s called Long Branch, which was originally a Summer Resort when founded in 1884: affluent families in downtown Toronto would take the street car to their summer “cottage” in Long Branch. It’s now just another bedroom community but only a 15-minute GO train ride from downtown Toronto.
Canada overall is a blessed place: we’re protected by two oceans and it’s nice having a friendly neighbor and military power to the south. The rest of the world probably considers us boring, which suits us fine: we’ll keep us a best-kept secret! At one point we considered Mexico as a way to avoid Canada’s long winter and relatively high taxes but the high apparent levels of crime in recent years scared us off. My parents were British and French so we like to visit the UK and France, as well as Spain. But we are happy to keep Toronto a home base and to visit places for months at a time through AirBnB.
REL: In your retirement life, what will you do about access to health care? Are you open to Medical Tourism?
JC: Again, Canada’s health care system is almost free for citizens and reasonably accessible. In fact, it’s so attractive that it may prevent some of us from permanently pulling up stakes. I can see Dental Tourism as more likely, as only recently have the NDP started to badger the Trudeau Liberals to provide universal free dental care for young people and low-income seniors.
Sadly, neither category is us!
REL: Are you a traveler or more of a stay-at-home, community kind of guy? Are you and your wife on the same page regarding retirement and travel?
JC: I think we are. Ruth retired from her full-time job in the transportation industry three years ago but still does a bit of consulting and a lot of church work, volunteering, tutoring and the like.

Lake Ontario, a 30-second walk from Jon and Ruth’s home
As I said to you before this interview, I still put in a “gruelling 3-hour day” Monday to Thursdays, with Friday mornings if necessary. Like yourselves, I can run the web site from anywhere with good Internet access. Most recently we spent 4 weeks in Malaga, Spain and I kept things going from there. But in our next stage we will try to avoid more of the long Canadian winter and spend 2 or 3 months at a time abroad in January/February/March. Continue Reading…