 By Mark and Joe
By Mark and Joe
Special to the Financial Independence Hub
The 4% rule is a common rule of thumb in many retirement planning circles, including the Financial Independence, Retire Early (FIRE) community in particular.
What does the 4% rule actually mean?
Should the 4% rule be used for any FIRE-seeker?
Does the 4% rule really matter to retirement planning at all?
Read on to find out our take, including what rules of thumb (if any) we’re using at Cashflows & Portfolios for our early retirement dreams.
The 4% rule is really a starting point for a safe withdrawal rate
Unlike 2 + 2 = 4, the 4% rule is not really a universal truth for any retirement plan at all.
It is, however, in our opinion, a great starting point to understand the impacts of asset decumulation, related to inflation, over time.
As you’ll read more about in the sections below, the 4% rule is fraught with many problems. None more so than for an early retiree or FIRE-seeker. In some cases, for the FIRE community, we believe the 4% rule should no longer be used at all.
Are any financial rules really rules?
Backing up, here is the source for the 4% rule.
The article from 1994!

Despite the geeky photo, by all accounts, Bill Bengen was one heckuva guy and a smart guy as well!
Potentially no other retirement planning rule of thumb has received more attention over the last 25-30 years than Bengen’s publication about the 4% rule. This publication in 1994 has triggered a new generation of devotees and arm-chair financial planners that are using this quick-math as a way to cement some retirement dreams. We believe that is a mistake for a few reasons.
First, let’s unpack what the 4% rule really means.
What does the 4% rule actually mean?
From the study:
“In Figures 1 (a)-l(d), a series of graphs illustrates the historical performance of portfolios consisting of 50-percent intermediate-term Treasury notes and 50-percent common stocks (an arbitrary asset allocation chosen for purposes of illustration). I have quantified portfolio performance in terms of “portfolio longevity”: how long the portfolio will last before all its investments have been exhausted by
withdrawals. This is an intuitive approach that is easy to explain to my clients, whose primary goal is making it through retirement without exhausting their funds, and whose secondary goal is accumulating wealth for their heirs.”
Unpacking this further, for those that do not want to read the entire study, here is something more succinct from Bengen:
Assuming a minimum requirement of 30 years of portfolio longevity, a first-year withdrawal of 4 percent, followed by inflation-adjusted withdrawals in subsequent years, should be safe.
“Should be safe”.
Again, the theory is one thing. Reality is something different and the financial future is always subject to change. Furthermore, if you’re blindly following this formula without considering whether it’s right for your situation, let alone putting in some guardrail approach to monitor your portfolio value at various checkpoints, you could end up either running out of money prematurely or being left with a huge financial surplus that you could have spent during your retirement. We’ll prove that point in a bit from another leading author.
Should the 4% rule be used for any FIRE-seeker?
Probably not. For many reasons.
Recently, Vanguard published an outstanding article about the need to revise any thinking about the 4% rule for the FIRE movement – a driver for this post.
Although the 4% rule remains a decent rule of thumb we believe most FIRE-seekers should heed the cautions in the Vanguard post. Here are some of our thoughts based on the article’s contents.
- Caution #1 – FIRE-seekers should not rely on past performance for future returns
We agree. In looking at this Vanguard set of assumptions below, and based on our own personal investing experiences, we believe historical returns should not be used to guarantee any future results.

Source: Vanguard article – Fueling the FIRE movement
While the FP Canada Standards Council doesn’t have a multi-year (10-year) return model in mind, they did highlight in their latest projection assumption guidelines that going forward, investor returns may not be as juicy as in years past.
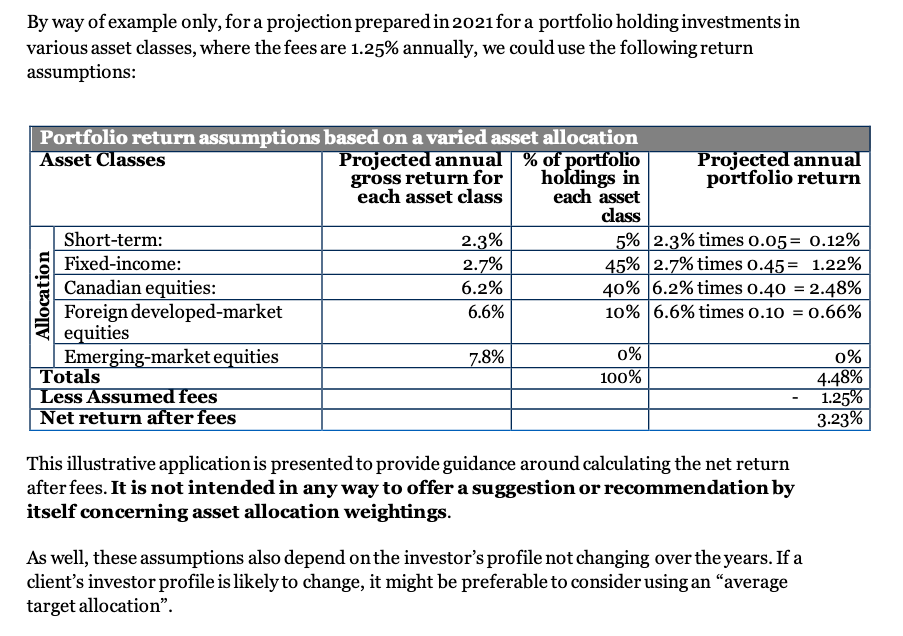
Source: FP Canada Standards Council.
This means for any historical studies, while interesting, may not be a great predictor of any future outcomes.
- Caution #2 – The FIRE-seeking time horizon is longer
Bengen noted in his 1994 study:
“Therefore, I counsel my clients to withdraw at no more than a four-percent rate during the early years of retirement, especially if they retire early (age 60 or younger). Assuming they have normal life expectancies, they should live at least 25-30 years. If they wish to leave some wealth to their heirs, their expected “portfolio lives” should be some longer than that. “
Bengen goes on to say:
“If the client expects to live another 30 years, I point out that the chart shows 31 scenario years when he would outlive his assets, and only 20 which would have been adequate for his purposes (as we shall see later, a different asset allocation would improve this, but it would still be uncomfortable, in my opinion).
This means he has less than a 40-percent chance to successfully negotiate retirement–not very good odds.”
To paraphrase, Bengen’s study was relevant to 30 years in retirement. Not 35 years. Not 40 years and certainly not 50 years like some FIRE-seekers may need if they plan to retire at age 40 and live to age 90 (or beyond).
This is simply a huge reminder that your time horizon is a critical factor when it comes to retirement planning.
- Caution #3 – FIRE-seekers may need to live with more stocks
Bengen’s 1994 study was based on the following:
“Note that my conclusions above were based on the assumption that the client continually rebalanced a portfolio of 50-percent common stocks and 50-percent intermediate-term Treasuries.” Continue Reading…










